Are You Eating The Right Amount Of Protein? Here’s What To Know

Consuming excessive amounts of protein can strain the kidneys, lead to dehydration, and increase the risk of developing osteoporosis. The body can only utilize a certain amount of protein at a time for muscle repair and growth, so consuming excessive amounts will not provide additional benefits.
The Institute of Medicine states that up to 35% of daily calories can come from protein without adverse effects for most healthy individuals. However, consistently exceeding this limit can have negative consequences on kidney function and overall health.
It’s important to strike a balance and consume protein within recommended guidelines based on individual needs and goals. Consulting with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian can help determine the appropriate protein intake for optimal health and performance.
In conclusion, protein is a vital nutrient for overall health, muscle growth, and weight management. Understanding the recommended intake for different goals and choosing high-quality protein sources is key to optimizing health and performance. By incorporating a variety of protein-rich foods into your diet and monitoring intake based on individual needs, you can ensure you are meeting your protein requirements for optimal health and well-being.
The Importance of Moderating Protein Intake for Optimal Health
When it comes to protein intake, more is not always better. While protein is essential for muscle growth, metabolism, and overall health, consuming excessively high amounts can have negative consequences. Extremely high protein intake, defined as above 3.0–4.0 g/kg of body weight, is generally unnecessary and could lead to a variety of issues.
Potential Risks of Excessive Protein Intake
- Digestive Issues: Consuming excessive amounts of protein can lead to digestive issues such as bloating and constipation. This is because the body may struggle to break down and digest large quantities of protein.
- Nutrient Imbalances: Excess protein intake may displace other essential nutrients in the diet. This can lead to deficiencies in vitamins, minerals, and other important micronutrients that are necessary for overall health.
- Potential Kidney Strain: Individuals with pre-existing kidney disease or impaired kidney function may be at risk of further strain on their kidneys with extremely high protein intake. The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products from protein metabolism, and excessive protein consumption can put additional stress on these organs.
Optimizing Protein Intake
It’s important to note that protein needs vary based on factors such as age, activity level, and individual goals. Whether you’re aiming for general health, muscle gain, or weight loss, focusing on high-quality protein sources and spreading your intake evenly across meals can help optimize muscle growth, metabolism, and recovery.
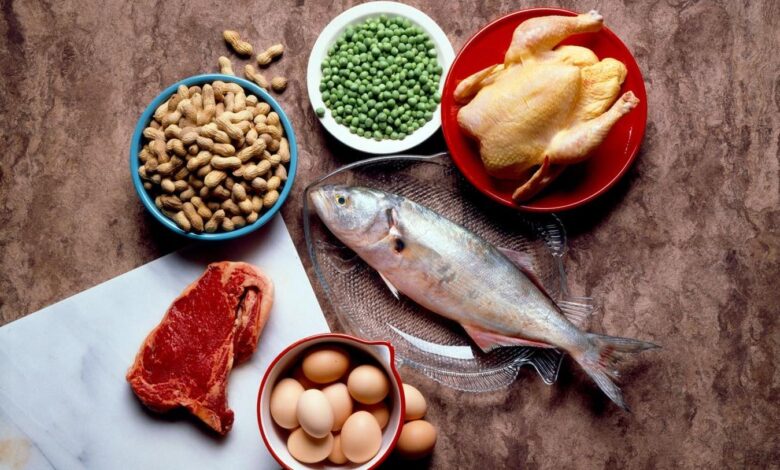
By choosing lean sources of protein such as poultry, fish, tofu, and legumes, you can meet your protein needs without overloading your body. Additionally, incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods into your diet can help ensure that you’re getting all the essential nutrients your body requires for optimal functioning.
Ultimately, moderation is key when it comes to protein intake. By listening to your body’s hunger cues and making mindful choices about the types and amounts of protein you consume, you can support your overall health and well-being without putting unnecessary strain on your digestive system or kidneys.